Kotlin vs Java - what's the difference between the two?
To study extra about Java get a free introduction to Java course at Make Android Apps.
Today, Android Studio ships with Kotlin assist built-in, so creating an Android venture that understands Kotlin code is as straightforward as deciding on a checkbox in Android Studio's venture creation wizard. Help has grown for the choice too additional time, to the purpose that this choice now primarily comes right down to desire.
However when you do swap Java to Kotlin, what precisely are you gaining? What options does Kotlin have, that Java doesn't, and vice versa?
On this article, we're going to be taking a look at all the main variations between Kotlin vs Java.
Kotlin vs Java, the later presents extra succinct code – with no findViewByIds
If you happen to evaluate a Kotlin class and a Java class which are performing the same work, then the Kotlin class will usually be rather more concise. However, there's one space precisely the place Kotlin can critically cut back the quantity of boilerplate code you want to write: findViewByIds. Kotlin Android Extensions mean you can import a reference to a View into your Exercise file, at which level you'll have the ability to work with that View as if it was a part of the Exercise. The outcome? You'll by no means have to write down one other findViewById methodology once more! Earlier than you need to use these extensions, you'll want to add a plugin to your module-level construct. Gradle file (apply plugin: 'kotlin-android-extensions') however after that you just are prepared to begin importing Views, for instance in case your activity_main.xml file contained a TextView with the ID textView, you then add the next to your Exercise:import kotlinx.android.artificial.fundamental.activity_main.textViewYou'll be able to enter later this TextView utilizing only its ID:
textView.setText("Good day World")
That is a lot extra succinct than the Java equal:
TextView textual content = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView); textual content.setText("Good day World");
Kotlin is null secure by default
NullPointerExceptions are an enormous supply of frustration for Java builders. Java permits you to assign null to any variable, however when you attempt to use an object reference that has a null worth, then brace your self to come across a NullPointerException!
Additionally learn: Kotiln for Android introduction
In Kotlin, every type is non-nullable (unable to carry a null worth) by default. If you happen to attempt to assign or return null in your Kotlin code, then it'll fail at compile-time, so neither of the next strains will compile:
val identify: String = null
enjoyable getName() : String = nullIf you happen to wish to assign a null worth to a variable in Kotlin, you then explicitly mark that variable as nullable, by including a query mark after the sort:
val quantity: Int? = nullThis makes it nearly not possible to come across NullPointerExceptions in Kotlin – in reality, when you do encounter this exception. The likelihood is it's since you explicitly requested Kotlin to throw one, or the NullPointerException is originating from exterior Java code.
Extension features
Kotlin offers builders the flexibility to increase a category with new performance, which is right if there's a category that you just all the time felt was lacking an essential methodology! These 'extension features' aren't out there in Java, though they're out there in different programming languages that you need to use for Android improvement, resembling C#.
Learn Subsequent: Java tutorial for beginners
You create an extension operate by prefixing the identity of the category you wish to lengthen (resembling 'String') to the character of the perform you're creating ('style string') for instance:
enjoyable String.styleString(): String {
// Fashion the string after which return it//
}
You'll be able to name this then work on cases of the prolonged class, through the. notation, as if it has been a part of that class:
myString.styleString()
Coroutines are first-class residents
Every time you provoke a long-running operation, resembling community I/O or CPU-intensive work, the calling thread is blocked till the process completes. Since Android is single-threaded by default, as quickly as you stick the first thread, your app's UI goes to freeze, and it'll stay unresponsive till the operation completes. In Java, the answer has historically been to create a background thread the place you'll be able to carry out this intensive or long-running work, however managing several threads can result in complicated, error-prone code, and creating a brand new thread is a costly operation. While you can create extra threads in Kotlin, you may also use coroutines. Coroutines carry out long-running and intensive duties by suspending execution at a certain level without blocking the thread, after which resuming this operate at a later level, probably on one other thread. This lets you create non-blocking asynchronous code that appears to be like synchronous, and is subsequently extra clear, concise and human-readable. Coroutines are additionally stackless so that they have a decrease reminiscence utilization in comparison with threads. So they open the door to other types of asynchronous non-blocking programming, resembling async/await.There aren't any checked exceptions
Kotlin doesn't have checked exceptions so that you don't must catch or declare any exceptions. Whether or not that is one thing that pulls you to Kotlin, or makes you wish to stick to Java will rely on your opinion of checked exceptions, as it is a function that divides the developer group. If you happen to sick of strive/catch blocks cluttering up your Java code, you then you are going to be proud of this omission, nonetheless, when you discover that checked exceptions encourage you to consider error restoration and finally push you in the direction of creating extra robust code, they're extra prone to see this as space the place Java has the sting over Kotlin.Native assist for delegation
Kotlin, not like Java, helps the "composition over inheritance" design sample, through first-class delegation (typically referred to as implicit delegation). The commission is the place a receiving object delegates operations to a second delegate object, which is a helper object with the unique context. Kotlin's class delegation is a choice to an inheritance that makes it potential to make use of heritage. In the meantime, Kotlin's delegated properties assist stop the duplication of code, for instance, if you want to reuse the identical code for several properties' getters and setters, then you'll be able to extract this code right into a delegated property. The property delegate must outline the getValue operator operate and, optionally, the setValue operator:class Delegate {
operator enjoyable getValue(...)
...
...
...
}
operator enjoyable setValue(...)
...
...
...
}
}
Then, if you're making a property you'll be able to declare that the getter and setter features for this specific property are dealt with by one other class:
class MyClass {
var property: String by Delegate()
}
Knowledge lessons
It's commonplace for a venture to have several experiences that do nothing, however, maintain information. In Java, you'll end up writing numerous boilerplate code for these lessons, though the experiences themselves have little or no performance. Usually, you'll outline a constructor, fields to retailer the info, getter and setter features for every discipline, plus hashCode(), equals() and toString() features. In Kotlin, when you embody the 'information' key phrase in your class definition, then the compiler will carry out all of this be just right for you, together with producing all the required getters and setters:information class Date(var month:String, var day: Int)
Sensible casts
In Java, you usually need to examine sort after which solid an object in conditions the place it's already clear that the article may be reliable. Kotlin's sensible casts can deal with these redundant casts for you, so that you don't must reliable inside an announcement when you've already checked it with Kotlin's 'is' operator. For instance, the compiler is aware of that the next solid is secure:if (whats up is String) {
printString(whats up)
}
Help for constructors
In contrast to Java, a Kotlin class can have a significant constructor and several secondary constructors, which you create by together with them in your class declaration:class MainActivity constructor(firstName: String) {
}
No assist for implicit widening conversions
Kotlin doesn't assist implicit widening conversions for numbers, so smaller varieties aren't implicitly transformed to more extensive types. In Kotlin, if you wish to assign a worth of sort Byte to an Int variable, you carry out a specific conversion, whereas Java has to assist for implicit conversions.Annotation processing libraries with Kotlin
Kotlin helps all current Java frameworks and libraries, together with superior structures that depend on annotation processing, though some Java libraries are already offering Kotlin extensions, resembling RxKotlin. If you happen to wish to use a Java library that depends on annotation processing, then including it to your Kotlin venture is barely totally different as you'll specify the dependency utilizing the kotlin-kapt plugin, after which use the Kotlin Annotation processing instrument (kapt) as an alternative of annotation processor. For instance://Apply the plugin//
apply plugin: 'kotlin-kapt'
//Add the respective dependencies utilizing the kapt configuration//
dependencies {
kapt "com.google.dagger:dagger-compiler:$dagger-version"
...
...
...
}
Interchangeability with Java
When debating whether or not to make use of Kotlin or Java for Android improvement, you have to be conscious that there's a 3rd choice: use each. Regardless of all of the variations between the two languages, Java and Kotlin, are 100% interoperable. You'll be able to name Kotlin code from Java, and you'll call Java code from Kotlin, so it's potential to have Kotlin and Java lessons side-by-side inside the similar venture, and the whole lot will nonetheless compile. This flexibility to manoeuvre between the two languages is helpful if you're getting began with Kotlin because it permits you to introduce Kotlin into a current venture incrementally. However, you might also favour making use of each language on an everlasting foundation. For instance, there could also be sure options that you prefer to write down in Kotlin and sure options that you discover simpler to write down in Java. Since Kotlin and Java each compile to bytecode, your end-users gained to have the ability to inform the place your Java code ends, and the Kotlin code begins, so there's no cause why you'll be able to launch an app that consists of Java and Kotlin code. If you happen to wish to strive Kotlin for your self, then so long as you will have Android Studio 3.0 Preview or increased put in, there are several methods which you can get began:- Create a brand new Android Studio venture. The most straightforward methodology is to create a brand new enterprise and choose the 'Embody Kotlin assist' checkbox from the venture creation wizard.

- Add a Kotlin class to a current listing. Management-click, the listing in the query, then choose 'File > New > Kotlin File/Class.' Android Studio will show a banner asking you to configure your venture to assist Kotlin; click on the 'Configure' hyperlink and observe the on-screen directions.
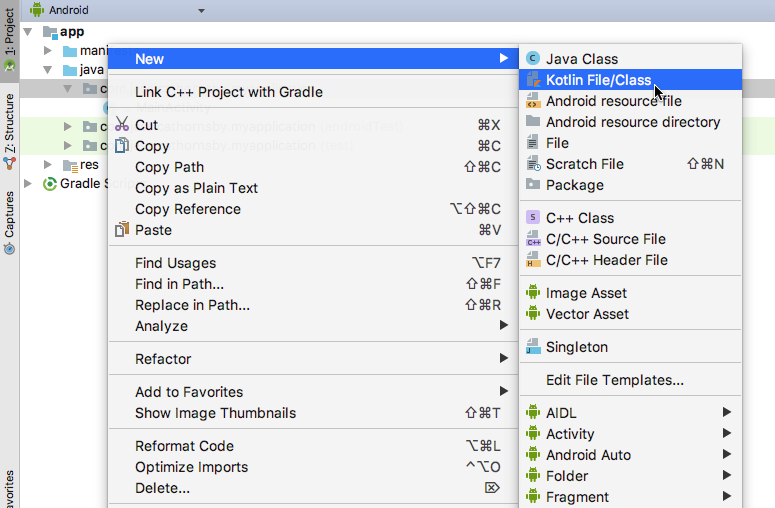
- Convert current Java records data to Kotlin. You'll be able to run any Java file using a Kotlin converter, by Management-clicking the file and deciding on 'Code > Convert Java File to Kotlin File.'




0 Comments